Singleton Design Pattern by example
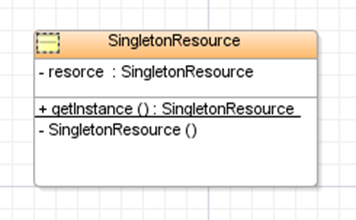
Singleton design pattern is most commonly used among all available java design patterns. It is a Creational patterns. Basic purpose of this design pattern is to maintain only one instance of a class throughout the application. This class may represent a common shared resource, functionality etc. When to Use ? You should consider singleton design pattern in following scenario A resource is shared across all application component and only one instance of resource is possible. Global variables are being passed across all part of application Multiple instances representing same kind of information. How to Use ? It is very simple to implement this design pattern. Following are he key requirements and possible solution for implementing singleton design pattern. Only one instance should be available at the time – restrict the class instantiation using private scoped constructor. Everybody should get same instance – maintain a private static instance variable ...
